When it comes to maintaining a bus fleet, there are two common approaches: preventive and predictive maintenance. Both are aimed at minimising downtime and reducing repair costs, but they differ in their methodology, with one guaranteeing better visibility over potential faults and greater opportunities for averting breakdowns.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between these two maintenance approaches and help you determine which one is best for your bus service.
What is preventive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance is a type of maintenance that involves regularly scheduled inspections and is performed at intervals, based on estimations of when a failure may occur, when a part replacement may be necessary, or even on drivers’ feedback.
It can be used by bus operators to ensure that their fleets are in good condition and reduce the risk of unexpected breakdowns that can lead to service disruptions and increased repair costs.
Preventive maintenance schedule
While implementing this maintenance approach, teams frequently establish a maintenance schedule based on mileage, time, or usage.
This schedule should include routine tasks like oil changes, tire rotations, brake inspections, and fluid checks. By performing these maintenance tasks regularly, teams can identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
Benefits of preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance contributes to extending the lifespan of vehicles, which are regularly checked for failures that may cause more serious problems in the future and lead to safety hazards.
This approach also enables service teams to catch potential issues before they result in unplanned downtime, thus controlling costs and improving the overall safety and reliability of transport services. However, preventive maintenance does not optimise cost, components’ life cycle nor vehicle planned downtime.
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is the most advanced approach to maintenance operations. It uses data analysis and machine learning to provide predictive insights that indicate when and if a repair will be needed, rather than relying on a pre-determined schedule.
By predicting when interventions are needed, operators can prevent unplanned downtime, plan ahead, and save on unnecessary costs.
Note: this approach is only possible when transport operators invest in the automated collection and processing of vehicle data.
Vehicle data
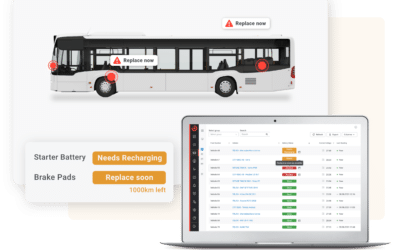
Today’s buses are vehicles of high sophistication. The data from the sensors that are built into the majority of their components and systems can be collected, analysed, and turned into predictive insights that can inform maintenance decisions, acting as early-warning systems.
In the context of a commercial bus fleet, operators may leverage predictive algorithms that indicate, based on real-time data, when components such as brake pads need to be replaced.
Benefits of predictive maintenance
The capability of alerting about risks ahead of time, and working as an early-warning system, makes predictive maintenance a significant paradigm shift in the way transport operators manage their operations.
By harnessing the power of data and artificial intelligence, this type of maintenance anticipates breakdowns and minimises unplanned downtime, resulting in maximised vehicle availability, as component failures can be averted before they cause service disruptions, unexpected costs, and damage passengers’ trust.
Additionally, by knowing beforehand when parts replacements will be needed, service teams can schedule maintenance for off-peak periods, order components in bulk, optimise stock management, and avoid unnecessary labour costs.
Finally, the automation capabilities of predictive maintenance are undoubtedly an advantage for maintenance personnel, as repetitive tasks like odometer readings, coolant checks, and the daily planning of distance-based service tasks (e.g. brake replacements) can be automated, thus saving time. More examples are mentioned in the image below.
Preventive maintenance vs Predictive maintenance – Pros and cons
A preventive maintenance approach can keep costs low and reduce unplanned downtime, but it can be resource-intensive and has some limitations, like not offering real visibility into the component’s remaining life, and not detecting potential issues that can become safety hazards.
Predictive maintenance is the only approach that can prevent unplanned downtime with accuracy while also saving costs in resources and in averted emergency repairs.
It differentiates from preventive maintenance by using real-time data to predict when maintenance will be needed and also differs by overcoming the variations that naturally occur between vehicles assigned to different routes and saving the time needed for visual inspections. Some of its cons are the necessity of having a dedicated person to analyse the data to fully leverage the benefits of the solution, and the initial cost of implementation.
What’s next?
Access our latest case study with the Keolis Group to find out more about how one of the world leaders in shared mobility, with operations in 14 countries, is leveraging Stratio’s Predictive Maintenance to keep costs low while increasing operational efficiency.
- Route-25 Project: Revolutionising Portugal’s Mobility Sector - September 25, 2024
- 6 Benefits of Implementing a Bus Maintenance Software - April 17, 2024
- Unlocking a more sustainable future with data-powered predictive maintenance - January 15, 2024