Public transport operators have the responsibility of ensuring that passengers have access to a safe and reliable service that connects them to critical services. Continuous maintenance and repairs are needed to maintain bus fleets operating smoothly, and unexpected breakdowns can disrupt service and cause delays.
The wear and tear on vehicles used as intensively as city buses, for example, can also be significant and may require frequent replacements of parts. Behind the scenes, service teams are the ones planning and executing maintenance plans, striving to continuously improve the reliability of transport services by minimizing downtime and preventing failures. Balancing the need for reliability and safety and the need to keep costs low is a critical challenge, which each transport operator approaches differently.
However, not all maintenance approaches were created equal, with some guaranteeing better visibility over potential faults and greater opportunities for averting breakdowns, as we will demonstrate below, by comparing Reactive, Preventive and Predictive Maintenance.
Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance happens when a problem has already occurred. Intuitively, reactive maintenance saves the cost of preventative servicing but can result in serious overspending for emergency repairs.
Not to mention the downtime that unexpected breakdowns cause, which not only impacts transport operators’ bottom line but, if frequent, can damage passengers’ trust and reduce revenue. In some cases, where the company doesn’t dispose of enough spare vehicles, renting a replacement bus may be necessary, further increasing the cost of a breakdown.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is performed at fixed intervals based on estimations of when a failure may occur, or when a part replacement may be necessary. Estimations are usually based on visual inspections and schedules that reflect an approximation of parts’ wear and tear.
This type of maintenance enables service teams to catch potential issues before they result in unplanned downtime, thus keeping costs low and improving the overall reliability of transport services. Proactive maintenance also contributes to extending the life of vehicles, which are regularly checked for failures that may cause a more serious problem in the future.
Predictive Maintenance
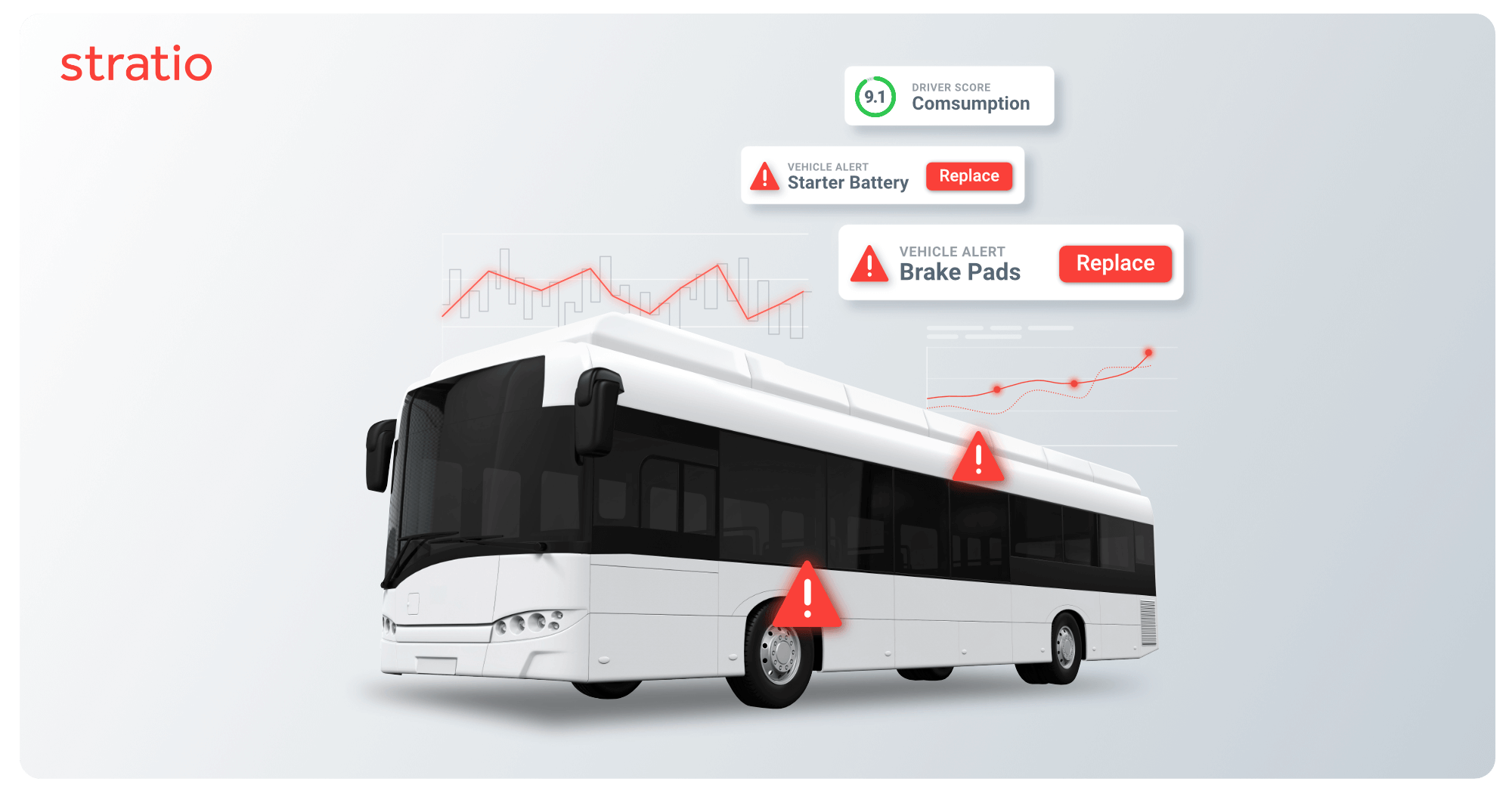
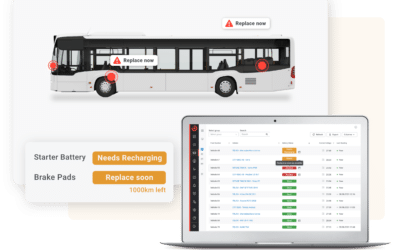
Predictive Maintenance is the most advanced approach to maintenance operations. It is possible only where transport operators invest in the automated collection and processing of vehicle technical data.
Today’s buses are vehicles of similar sophistication to Formula 1 cars. The data that the sensors that are built into the majority of components and systems can be collected, analyzed and turned into predictive insights that can inform maintenance decisions. In the context of a commercial bus fleet, operators may leverage predictive algorithms that indicate, based on real-time data, when brake pads need to be replaced.
Predictive maintenance differs from preventive in that it overcomes the variations that naturally occur between vehicles assigned to different routes and saves the time needed for visual inspections. A city bus, for instance, brakes much more often than a longer haul, intercity vehicle.
With AI Predictive maintenance, transport operators can rely on AI predictive algorithms to spot patterns in the data collected that indicate if and when a replacement will be needed. Additionally, by predicting when the brake pads will need to be replaced, operators can schedule maintenance during off-peak periods, reducing downtime and minimizing the impact on operations.
Reactive vs Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance: Conclusions
Reactive maintenance may save costs in the short term but may result in serious overspending for emergency repairs. Preventive maintenance is more effective at keeping costs low and reducing unplanned downtime but can be resource-intensive and presents some limitations.
AI Predictive maintenance is the only approach that can prevent unplanned downtime with accuracy while also saving costs in resources and in averted emergency repairs. It can be a game changer for operators interested in the digitization of what used to be time-consuming, error-prone, manual work. By eliminating unplanned downtime, operators can also increase the reliability of the service offered to passengers, creating a virtuous cycle of savings and increased revenue.
- Route-25 Project: Revolutionising Portugal’s Mobility Sector - September 25, 2024
- 6 Benefits of Implementing a Bus Maintenance Software - April 17, 2024
- Unlocking a more sustainable future with data-powered predictive maintenance - January 15, 2024