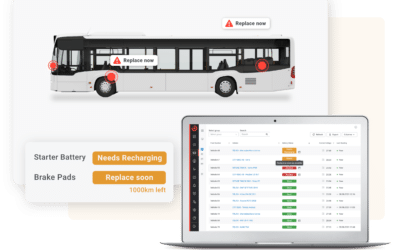
The world’s largest transport operators leverage Predictive Maintenance to keep their vehicles on the road and offer a service without disruptions. This maintenance approach uses AI predictive algorithms to spot patterns in the data collected from sensors to indicate when a replacement will be needed, allowing service teams to plan ahead and schedule repairs before a breakdown occurs.
But how did transport operators like Keolis, Go Ahead, and Arriva change their processes to make the most of a predictive maintenance approach? Which tasks are they able to automate? And what parameters does a predictive maintenance solution monitor?
To clarify what transport operators can expect from a predictive maintenance solution, we have compiled a list of the 5 most commonly asked questions about this maintenance strategy.
1. Does a Predictive Maintenance solution automate everything?
In short, no. A predictive maintenance solution doesn’t eliminate the need for a solid service team and knowledgeable engineers to perform high-value tasks.
With predictive maintenance, however, transport operators can automate repetitive tasks such as odometer readings, coolant checks, and the daily planning of distance-based service tasks (e.g., oil changes and brake replacements). Predictive maintenance also enables better intervention planning, as it proactively alerts the team of risks ahead of time.
2. Do I need to change processes to make the most of Predictive Maintenance?
Yes and no. Any maintenance team would benefit from having increased visibility over vehicles’ conditions, whether in the form of predictive insights and early warnings that can inform the scheduling of replacements and servicing or remote diagnostics.
But to make the most of a predictive maintenance solution, operators should implement changes that enable teams to leverage the predictive capabilities. These may include adopting an asset management system or creating a dedicated position to leverage the data and make strategic decisions about the fleet.
3. How does Predictive Maintenance intersect with Fleet Management?
Predictive maintenance contributes to fleet management. It helps fleet management teams decide when to schedule maintenance and repairs, leading to better fleet utilisation and cost savings.
Predictive maintenance, however, aims to prevent equipment failure and reduce unplanned downtime rather than optimising usage and utilisation, reducing operating costs, and other tasks related to asset management.
4. Which parameters does the typical Predictive Maintenance solution monitor?
A typical predictive maintenance solution for public transport monitors vehicle performance metrics, such as speed, fuel consumption, and engine performance. Thus, data requirements include:
- Maintenance and repair historical data, including information about past repairs and parts replacements;
- Condition monitoring data from sensors, such as level and temperature sensors;
- Wear and tear data, such as brake wear, and battery health, to estimate state-of-health and remaining useful life of components;
- Environmental factors, such as temperature or humidity, may affect vehicle performance;
- Usage data, such as the number of trips, miles driven, and hours of operation.
Another critical parameter that predictive maintenance solutions must track is feedback on alerts and reported malfunctions.
Thus, predictive maintenance relies on a continuous information loop between a predictive maintenance provider and the customer, where information flows both ways. That is a critical requirement for AI to adjust and continuously improve over time.
5. What’s the difference between Remote Diagnostics and Predictive Maintenance?
Remote diagnostics refers to the use of technology to remotely monitor and diagnose problems as they happen in equipment or vehicles. This involves collecting data from sensors and other sources and using it to manually detect issues and faults in real-time.
The goal of remote diagnostics is to quickly identify and fix problems, reducing downtime and quickly putting the vehicle back in operation. Thus, remote diagnostics optimise the resolution time for known problems after the fact.
Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, is an early warning system. It is a proactive maintenance strategy that uses data and analytics to predict if and when a piece of equipment or vehicle is likely to fail.
It optimises detection time and enables early intervention and effective risk mitigation strategies by signalling risks before they materialise.
Scheduled intervention is also more resource efficient from a procurement, labour, and planning perspective. Ideally, predictive maintenance and effective interventions combine to maximise uptime throughout an asset’s life cycle.
Final Thoughts
Access our latest case study with the Keolis Group to find out more about how one of the world leaders in shared mobility is leveraging Stratio’s Predictive Maintenance to keep costs low while increasing operational efficiency.
- 6 Benefits of Implementing a Bus Maintenance Software - April 17, 2024
- Unlocking a more sustainable future with data-powered predictive maintenance - January 15, 2024
- How Can Artificial Intelligence Support Public Transport Operators? - September 20, 2023